What is Net Asset Value (NAV)?
Net Asset Value (NAV) is a term applied to companies, funds, partnerships, trusts or other investment entities that describes the current value of the entity, usually expressed on a per-share basis. In simple terms, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission defines Net Asset Value as “a company’s total assets minus its total liabilities”.
Funds will typically hold dozens, if not hundreds, of financial assets on behalf of their investors. A Net Asset Value calculation sums the value of all the assets, subtracts the value of any liabilities, and provides investors with a way to determine the value of their shares.
For public funds (open-end investment companies), NAVs represent the exact price an investor can buy or sell shares, subject to any applicable sales charges or transaction fees. For closed-end fund entities, the price of a share is determined in the marketplace and may be above or below the calculated NAV.
Key Takeaways
- NAV is the current net value of an investor’s share of a fund or other investment entity.
- The market price of closed-end fund entities that trade in a public marketplace may vary from the calculated NAV.
NAV in Private Equity
In private equity funds, NAV represents the value of an investor’s shares in the fund at any particular time. Assets that have already been distributed to investors would not be included in the NAV. The values of all the holdings in a fund plus any other assets, such as cash, minus any unpaid expenses will represent the total NAV for the fund.
The values of the individual holdings in a private equity fund are determined by the general partner and updated quarterly using methods of valuation prescribed by the industry.
PE Fund Valuation
Since private equity shares do not trade on public exchanges, NAV is an important valuation measure for both the investors and the general partner.
Investors can gauge how their investment is going from the progression of a fund’s NAV over time. The NAV can essentially be interpreted as a measure of the residual value of investments held by the fund. Adding the NAV to any distributions already received from the fund will give investors a picture of how the total investment is progressing.
General partners use the fund’s NAV in determining the price for potential secondary transactions to third parties. Secondary transactions are important to general partners as a way of liquidating private company assets that have not gone public or been acquired in order to return capital to investors.
NAV Formula and Calculation
The formula for calculating NAV is as follows:
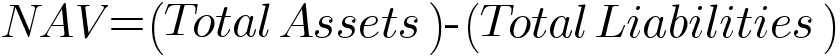
Where:
Total Assets represent the sum of the values of all assets held by the entity on behalf of its investors.
Total Liabilities represent the total of all liabilities, including borrowed capital, etc.
How to calculate NAV: An example
Let’s assume the following data for a hypothetical private equity fund:
| Assets | Value |
|---|---|
| Undistributed cash | $ 1,000,000 |
| Shares in company A | $ 8,300,000 |
| Shares in company B | $ 6,600,000 |
| Shares in company C | $ 9,720,000 |
| Shares in company D | $ 4,650,000 |
| Shares in company E | $ 3,930,000 |
| Total Assets | $34,200,000 |
| Liabilities | Value |
| Debt Outstanding | $6,400,000 |
| Carried Interest | $ 800,000 |
| Total Liabilities | $7,200,000 |
| Shares outstanding | 500,000 |
The Net Asset Value for this example is calculated as follows:
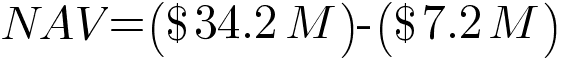
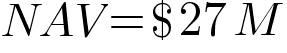
This would represent fund-level NAV. To obtain the per-share NAV, we must divide this by the number of outstanding shares as follows:
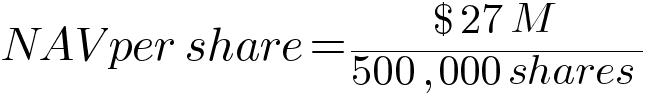
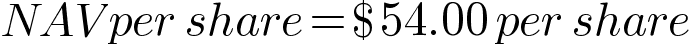
Net Asset Value FAQs
Is Net Asset Value the same as equity?
For a private equity fund, NAV would represent the net investor’s equity, yes. Both terms represent the net value of total assets less liabilities. Equity, however, is a much broader term that is also used to describe ownership in a variety of entities including corporations, trusts and partnerships as well as the entire asset class of corporate stocks.
Why is NAV important?
For mutual fund investors, NAV is important in that it represents the price an investor can actually buy or sell shares. In a closed-end fund that trades in a public marketplace, NAV represents the value of a fund’s assets, which can be compared to the market price to determine whether the market value is at a premium or discount to the fund’s intrinsic value.
For a private equity fund, NAV provides investors with a measure of a fund’s residual value and can be added to any prior distributions to determine the fund’s performance to date. For the fund’s general partner, the NAV can be used to determine the price at which assets in the fund can be sold as secondaries.
Related article: NAV Lending: What it is and why it's more relevant than ever
Which one is better: A higher or lower NAV?
The question cannot be answered in isolation. In a private equity fund, NAV rises as investments appreciate in value and declines as distributions are made to investors. As such, it cannot be determined whether a NAV is good or bad until distributions are added to it. When that is done, a higher total number is always better.
How is the net asset value (NAV) associated with a fund investment determined?
NAVs reflect the value of an investor’s stake in a private equity fund. Fund managers report NAV to their investors quarterly in accordance with strict valuation guidelines. The fund managers Moonfare works with are large organizations with large investors such as life insurance companies and pension funds, who have high standards with regard to accuracy and control of the valuation process. Moonfare and its investors benefit from these high standards. The NAV reported to our investors additionally includes any potential cash reserves and liabilities of the feeder vehicles.
How are remaining capital commitments considered with respect to net asset value (NAV)?
Buyers and sellers on the secondary market use NAV as a reference for pricing the stake involved in their transactions. The buyer assumes the obligation to meet the remaining capital commitments in full.
